这是arxiv上的一个占坑文吧。好像也没有写出后续。
Tossou A C Y, Dimitrakakis C. On The Differential Privacy of Thompson Sampling With Gaussian Prior[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:1806.09192, 2018.
主要结论是说基于高斯先验的TS算法 ([1]中的算法2) 已经是满足DP的。
保持饥饿,保持傻x 😄
这是arxiv上的一个占坑文吧。好像也没有写出后续。
Tossou A C Y, Dimitrakakis C. On The Differential Privacy of Thompson Sampling With Gaussian Prior[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:1806.09192, 2018.
主要结论是说基于高斯先验的TS算法 ([1]中的算法2) 已经是满足DP的。
#####Q1: 采样在机器学习中的应用?
A1: 采样本质是对随机现象的模拟,即根据给定的概率分布,模拟产生对应的随机事件。
采样也可以看作是一种非参数模型,即用较少量的样本点来近似总体分布,并刻画分布中的不确定性。这个角度考虑,也可以当作一种信息降维。
常见的如自助法和刀切法(Jack knife),通过对样本的多次重采样来估计统计量的偏差、方差等信息。重采样来处理分类模型的训练样本不均衡问题。
苹果Differential Privacy Team写的Learning with Privacy at Scale。介绍了苹果是怎么把差分隐私用在iOS中的。
Our system is designed to be opt-in and transparent. No data is recorded or transmitted before the user explicitly chooses to report usage information. Data is privatized on the user’s device using event-level differential privacy [4] in the local model where an event might be, for example, a user typing an emoji. Additionally, we restrict the number of transmitted privatized events per use case. The transmission to the server occurs over an encrypted channel once per day, with no device identifiers. The records arrive on a restricted-access server where IP identifiers are immediately discarded, and any association between multiple records is also discarded. At this point, we cannot distinguish, for example, if an emoji record and a Safari web domain record came from the same user. The records are processed to compute statistics. These aggregate statistics are then shared internally with the relevant teams at Apple.
用了local-DP,传输是每天一次,通过加密隧道传输的,去掉了唯一标识的信息比如IP,去掉了多个记录之间的相互联系。这样看来的确是很强的保护了隐私。
Kharitonov E. Federated Online Learning to Rank with Evolution Strategies[C]//Proceedings of the Twelfth ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining. ACM, 2019: 249-257.
WSDM, CCF B类会议, 数据库方向。
In this work, we consider Federated Online Learning to Rank setup (FOLtR) where on-mobile ranking models are trained in a way that respects the users’ privacy. We require that non-privatized user data, such as queries, results, and their feature representations are never communicated for the purpose of the ranker’s training. We believe this setup is interesting, as it combines unique requirements for the learning algorithm: (a) preserving the user privacy, (b) low communication and computation costs, (c) learning from noisy bandit feedback, and (d) learning with non-continuous ranking quality measures.
考虑联邦在线学习进行排名,其中移动排名模型以尊重用户隐私的方式进行培训。(斜体这句为什么说需要非隐私数据never用来做排名的训练?)
Hamm J, Cao Y, Belkin M. Learning privately from multiparty data[C]//International Conference on Machine Learning. 2016: 555-563.
在多方场景下,怎样在不获取其他party’s private data的情况下,通过组合本地训练的分类器,训练一个准确的符合DP的分类模型?本文提出了
transfer the ‘knowledge’ of the local classifier ensemble by first creating labeled data from auxiliary unlabeled data, and then train a global $\epsilon$-differentially private classifier.
本文指出大部分的voting都太敏感,因此提出了新的risk weighted by class probabilities estimated from the ensemble。相对于非隐私的方案,误差控制在$O(\epsilon^{-2} M^{-2})$之内,$M$是parties的数量。
Yao大佬在1986年提出的。可以叫多方安全计算的基石。
主要思想是离散的、fixed-size function可以转化为逻辑门电路,如果有一种可以安全地计算这个电路的方法,那么就可以安全地计算对应的function。
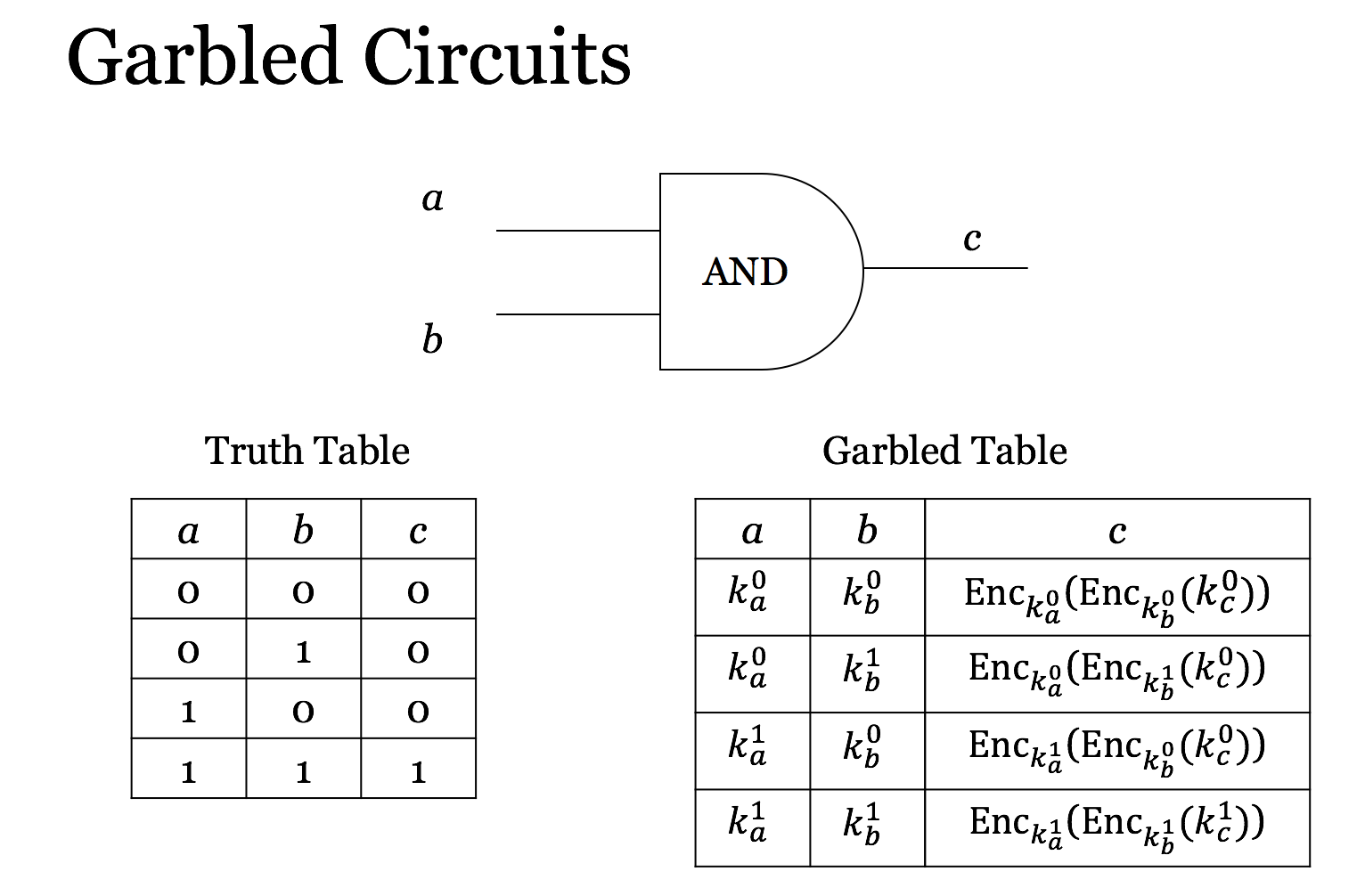
以AND function(与门)为例,实际上可以看成是一张真值表,如上图所示,两个输入同为1时,输出才为1;否则输出为0。