Abernethy J D, Jung Y H, Lee C, et al. Online Learning via the Differential Privacy Lens[C]//Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. 2019: 8892-8902.
Abstract
DP框架”less about privacy and more about algorithmic stability”。本文提出一种one-step differential stability,便于对在线学习进行更精细的regret分析。这种稳定性的提法对于follow-the-perturbed-leader算法的一阶regret bounds十分适用,这也是以前工作留下的问题。同时,本文提出了一种标准的max-divergence来得到更为宽广的一类Tsallis max-divergences。
Introduction
本文采用DP lens来设计和分析随机的在线学习算法,包括两种不同场景中:full information (online convex optimization, online linear optimization, experts problem) 和 partial information (multi-armed bandits, bandits with expert)。
Our rich set of examples suggests that our framework will be useful in translating results from the DP literature to study a much larger variety of online learning problems in the future.
本文的目标不是设计low-regret算法来满足privacy保证,而是以DP启发的基于稳定性的方法非常适合设计具有出色保证的在线学习算法。
Our goal is instead to show that, in and of itself, a DP-inspired stability-based methodology is quite well-suited to designing online learning algorithms with excellent guarantees.
文献[7 Noga Alon, Roi Livni, Maryanthe Malliaris, and Shay Moran. Private PAC learning implies finite Littlestone dimension. In Proceedings of the 51st Annual ACM SIGACT Symposium on Theory of Computing, pages 852–860. ACM, 2019.] 指出如果某类函数是可以privately learnable的,那么这个函数通过非构造性参数就有有限的Littlestone dimension(一个表征在线二进制分类的可学习性的参数)。我们的结果可以被解释为以建设性的方式证明了类似的主张,尽管是针对不同的、更容易解决的在线学习问题。
主要贡献是:
- 定义了one-step differential stability(定义2.1和2.2),得出一个关键引理,表明它如何产生一阶regret界限;
- 对[23 DanielKifer,AdamSmith,andAbhradeepThakurta.Privateconvexempiricalriskminimization and high-dimensional regression. In Conference on Learning Theory, pages 25–1, 2012.]中的目标扰动方法,针对OCO(定理3.2)和OLO问题(推论3.3)提出了具有一阶界限的新算法;
- 引入了一个新的Tsallis $\gamma$-最大散度族,以确保与标准最大散度相比具有更严格的稳定性;
- 通过使用各种扰动的新FTPL算法,我们为专家问题提供了最佳一阶界(定理3.6);
- 对multi-armed bandit算法的统一分析不仅统一了过去使用的大量扰动和正则化器的处理方法,而且揭示了由它们引起的微分稳定性的确切类型(定理4.2);
- 针对有专家的多臂赌博机问题,提出了新的算法,可以实现与EXP4算法[9 Peter Auer, Nicolo Cesa-Bianchi, Yoav Freund, and Robert E Schapire. The nonstochastic multiarmed bandit problem. SIAM journal on computing, 32(1):48–77, 2002.]相同的0阶和1阶界限。
Stability notitions motivated by DP
有一些研究统计学习算法稳定性分析的工作,但是很少有工作研究稳定性条件下的low regret online algorithm。本文主要用DP作为稳定性概念【Cynthia Dwork and Aaron Roth. The algorithmic foundations of differential privacy. Founda- tions and Trends in Theoretical Computer Science, 9(3-4):211–407, 2014. 13.2节 ,对小扰动要具有稳定性,这是DP的标志】。
DP通过以下散度来量化稳定性:P,Q是概率空间中的两个分布,P和Q之间的$\delta$-approximate max-divergence定义如下:
\[D_{\infin}^{\delta}(P,Q)=\sup_{P(B)>\delta}\log\frac{P(B)-\delta}{Q(B)}\]where the supremum is taken over measurable sets B。要指出最大散度不是一种metric,因为它不对称而且不满足三角不等式。
接下来定义了在线学习的稳定性,量化了对于新的损失函数,算法的分布会发生多少变化。
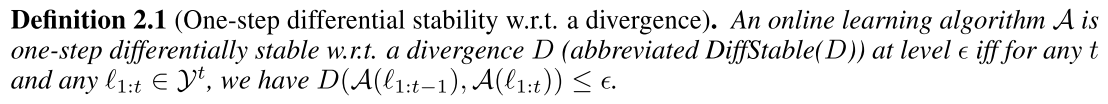
Key Lemma
下面引理很简单但是很强大。因为,首先,它使DP中大量的算法工作可用于推导regret界限;其次,DP算法经常添加扰动以实现隐私。

