DP-SGD主要是利用了差分隐私对梯度下降过程进行扰动,以达到学习出一个满足差分隐私的模型:Song S, Chaudhuri K, Sarwate A D. Stochastic gradient descent with differentially private updates[C]//2013 IEEE Global Conference on Signal and Information Processing. IEEE, 2013: 245-248.
Stochastic Gradient Descent
训练线性分类器就是解决如下的凸优化问题:
\[w^{*}=\underset{w \in \mathbb{R}^{d}}{\operatorname{argmin}} \frac{\lambda}{2}\|w\|^{2}+\frac{1}{n} \sum_{i=1}^{n} \ell\left(w, x_{i}, y_{i}\right)\]SGD的表达式如下:
\[w_{t+1}=w_{t}-\eta_{t}\left(\lambda w_{t}+\nabla \ell\left(w_{t}, x_{t}, y_{t}\right)\right)\]SGD with mini-batch:
\[w_{t+1}=w_{t}-\eta_{t}\left(\lambda w_{t}+\frac{1}{b} \sum_{\left(x_{i}, y_{i}\right) \in B_{t}} \nabla \ell\left(w_{t}, x_{i}, y_{i}\right)\right)\]DP-SGD
每次更新时,在梯度上加入噪声,以实现满足$\epsilon$-DP的算法。
\(w_{t+1}=w_{t}-\eta_{t}\left(\lambda w_{t}+\nabla \ell\left(w_{t}, x_{t}, y_{t}\right)+Z_{t}\right)\),
其中$Z_t\sim \mathbb{R}^d$是服从以下概率密度的随机向量,
\(\rho(z) \propto e^{-(\alpha / 2)\|z\|}\).
如果是对朴素的SGD来说,每次计算梯度用一个样本可以保证互斥,但是可以很直观地想象到,对每一个梯度加噪声的话,势必会造成梯度方向的混乱,能不能收敛都未必能保证,所以作者采用了batch的形式。
对于mini-batch来说,其形式如下
\(w_{t+1}=w_{t}-\eta_{t}\left(\lambda w_{t}+\frac{1}{b} \sum_{\left(x_{i}, y_{i}\right) \in B_{t}} \nabla \ell\left(w_{t}, x_{i}, y_{i}\right)+\frac{1}{b} Z_{t}\right) \tag{1}\).
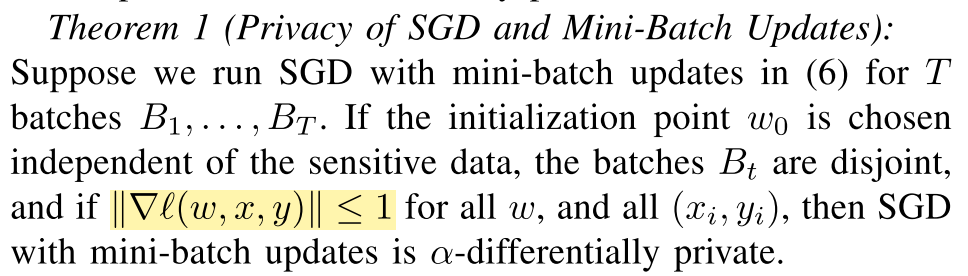
定理将梯度进行了bound,$|\nabla \ell(w, x, y)| \leq 1$,每次更新的全局敏感度就是$\frac{2 \eta_{t}}{b}$。然后算法需要保证每次用的batch是互斥的集合,这样不会降低隐私保证。但是虽然是batch的形式,减少了迭代次数从而降低噪声量产生的影响,直观感觉效果也不会很好,甚至怎么能保证一定收敛呢。
Experiments
Our synthetic dataset consists of n = 10, 000 samples drawn uniformly from a 5-dimensional sphere, and is linearly separable with margin 0.001. For our first classification task on real data, we use the KDDCup99 dataset, an intrusion detection dataset on network connections.We use a reduced dimension of d =9 for KDDCup, and d = 15 for MNIST.
We use SGD to train a logistic regression model. For each update, we use the mini-batch update from (2) for batch sizes $b \in {1, 2, 5, 10, 20, 50}$, with regularization parameter $\lambda =0.0001$ and $\alpha =1$. In each case, we make a single pass over the entire training data. To maintain numerical stability, after each update, we project the iterate $w_t$ onto a ball of radius $1/\lambda$.
For each experiment we investigated a few different schemes for setting the learning rates. We averaged the objective function values obtained over 20 random permutations of the training data as well as fresh random samples of the noise $Z_t$ for the private algorithm. The error bars are at a single standard deviation. Since we are interested in the optimization performance, we plot the objective function value.
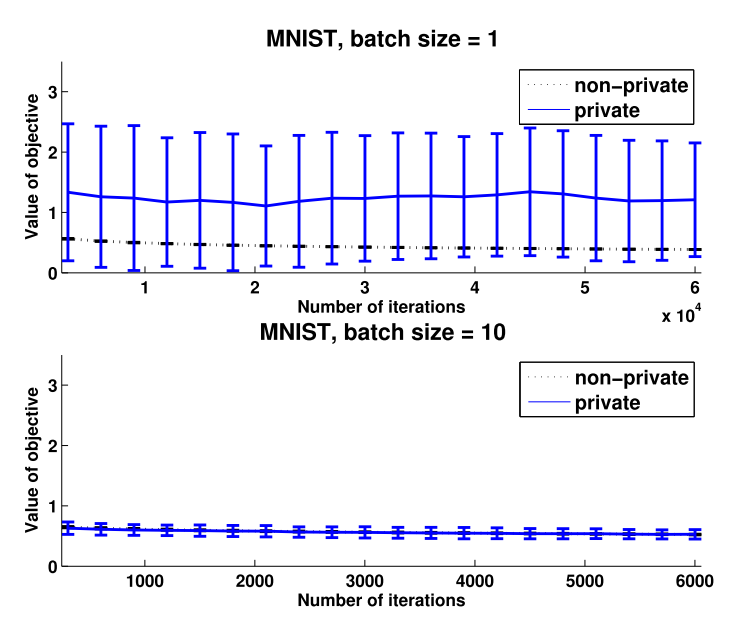
上图的学习率设置为$\eta_{t}=1 / \sqrt{t}$。可以看出,当batch size为1时,也就是朴素SGD,DP版本的离非隐私保护版本的相差甚远;当batch size为10时,效果就很好。
Conclusion[1]
放上大佬的结论,确实很有启发性。可以从这个角度去想一下是不是可以搞新方法出来。
1 - reduce over-fitting <-> privacy
其实上面关于正则项和增量数据集的实验摆到一起来,我们可以看到抑制过拟合与差分隐私之间的那种微妙的一致性。抑制过拟合的目的是避免模型偏离数据的泛化特征,学到数据集的局部特征,而差分隐私是希望减少个体数据对最终模型的影响。从上面两点来看,正则项和增量数据集两种抑制过拟合的方法都能够提高privateERM的性能。
这不禁令人浮想联翩,那么,其它的抑制过拟合的方法呢?要知道差分隐私方法最大的痛处就是添加的噪声会降低模型的性能,以致失去实用性,若是能够通过加入减少过拟合的方法来引出隐私保护,那么对于差分隐私方法的性能提升将是非常有意义的。
之后也有看到利用dropout来实现差分隐私的方法。[(Beyza Ermis, 2017)]
当然了,这里还有很多种可能。
2 - methods without sensitivity
目标扰动方法通过在目标函数中加入随机噪声来构建输出模型的随机性以实现差分隐私。这种方法比较有意思在它跳出了函数敏感度的桎梏,怎么来设计新的dp mechanism也是一块荒原啊。
Reference
[1] 满足差分隐私的经验误差最小化方法
